Unraveling the Mystery of AI Nanopores: Simulating Complex Flow Dynamics
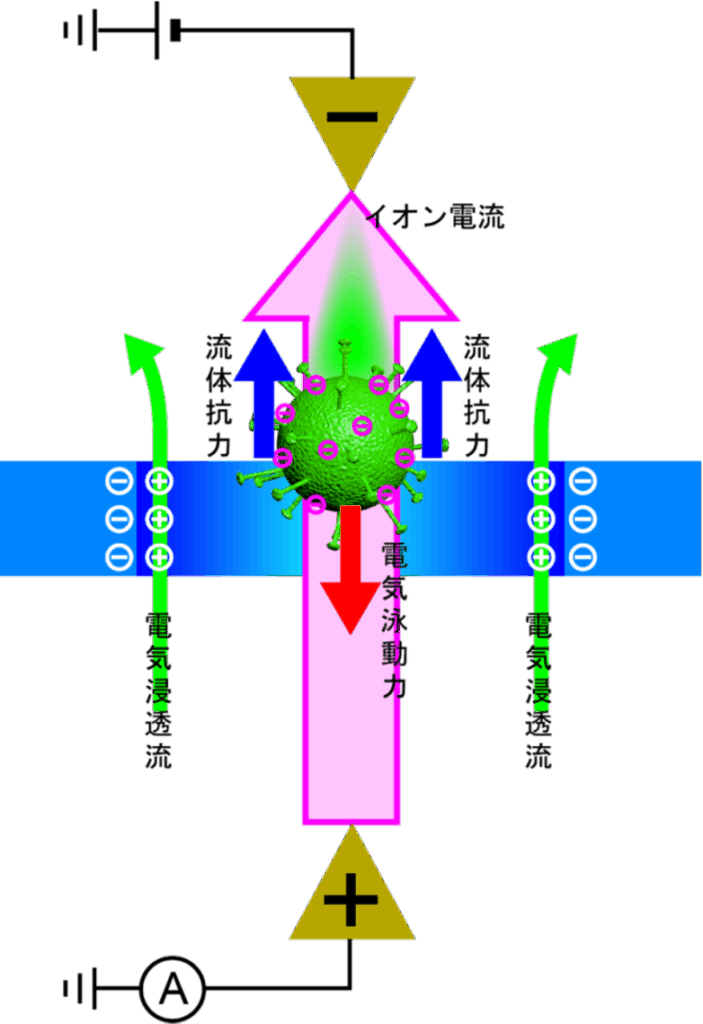
At first glance, a nanopore appears to be nothing more than a tiny hole drilled into a silicon substrate. Its diameter is typically less than a few hundred nanometers. However, the flow dynamics of matter passing through this tiny pore are extraordinarily complex. For example, when a single negatively charged nanoparticle attempts to pass through a nanopore, the following three forces act on it simultaneously.
Electrophoretic force: A force that pulls the particle toward the positive electrode when a voltage is applied
Electroosmotic flow: The motion of liquid inside the nanopore driven by an electric field
Hydrodynamic drag: Resistance exerted by the surrounding liquid
Conventional science has attempted to explain complex phenomena using individual, simplified theories. However, at the nanoscale, these effects do not act independently—they strongly interact with one another. Therefore, to elucidate the dynamics inside a nanopore, it is necessary to solve the equations describing all three forces simultaneously.
Development of Multiphysics Simulations
To address this challenge, we developed a method known as multiphysics simulation, which allows these three phenomena to be calculated at the same time. Using this approach, we can accurately simulate the ionic current flowing through a nanopore, as well as the temporal changes in ionic current that occur when a nanoparticle translocates through the pore (ionic current–time waveforms). As a result of these simulations, we discovered that ionic current–time waveforms contain crucial information about the nanoparticle, including its volume, structure, and surface charge. This finding directly led to the development of techniques that use AI to analyze these waveforms.
Future Perspectives: Integrating Data Assimilation
Research on time-dependent simulations of nanopore dynamics is still a largely unexplored field. A well-known example of simulations involving multiple intertwined complex phenomena is weather forecasting. In meteorology, a technique called data assimilation is used, in which real observational data and simulation results are integrated using AI.
By incorporating the concept of data assimilation into multiphysics simulations, we aim to further accelerate nanopore research and deepen our understanding of nanoscale transport phenomena.